Unlock Vital Information on Blood Tests to Detect Nutritional Deficiencies
What exactly is meant by a nutritional deficiency?
Understanding how to obtain a blood test for nutritional deficiencies is essential, as these deficiencies arise when the body lacks critical vitamins or minerals. This insufficiency can result in various health issues, including chronic fatigue and a compromised immune system. Within the UK, several prevalent deficiencies have been recognised, which include:
- Vitamin D: This vital vitamin is crucial for maintaining strong bones and supporting effective immune function.
- Iron: An essential mineral that plays a key role in the transport of oxygen throughout the body.
- Vitamin B12: This nutrient is vital for ensuring the proper functioning of nerves and the production of red blood cells.
- Folate: Critical for DNA synthesis and effective cell division, folate is indispensable for maintaining overall health.
- Magnesium: An important mineral that supports both muscle and nerve function.
- Zinc: This mineral is essential for preserving immune health and aiding in the healing of wounds.
- Calcium: Crucial for bone strength and muscle function, calcium is a key nutrient for overall health.
- Vitamin C: Important for maintaining skin health and bolstering the immune system, vitamin C is vital for overall well-being.
Identifying these deficiencies is fundamental for maintaining health and enhancing well-being.
What variety of blood tests are offered by UK healthcare services?
In the UK, various blood tests are available to detect nutritional deficiencies, primarily through the NHS or private healthcare providers. Common tests include serum ferritin (to evaluate iron levels), vitamin D tests, and a full blood count (FBC), which assesses overall nutrient levels in the body.
Additional tests may include:
- Serum Ferritin: This test measures the amount of stored iron in the body.
- Vitamin D Test: Evaluates the concentration of vitamin D in the bloodstream.
- Vitamin B12 and Folate Tests: Assess critical nutrient levels necessary for neurological function and red blood cell production.
- Thyroid Function Tests: Occasionally included to rule out any thyroid-related issues that may impact nutrient absorption.
These tests enable healthcare professionals to identify deficiencies and develop personalised treatment plans to meet individual needs.
How should you prepare for your upcoming blood test appointment?
Proper preparation for a blood test is crucial to ensure accurate results. In the UK, patients are often advised to fast before specific tests, particularly those evaluating glucose or lipid profiles. Consulting your GP beforehand to clarify any specific requirements prior to the test is essential.
Before your appointment, consider these crucial steps:
- Discuss Symptoms: Inform your GP of any symptoms you are experiencing, as this information can significantly influence the testing process.
- Medication Review: Provide a detailed list of medications you are currently taking, as some may affect your test results.
- Fasting Requirements: Follow any fasting instructions given, typically requiring 8-12 hours before the test for optimal accuracy.
- Hydration: Make sure to drink plenty of water before the test, unless otherwise advised, as staying hydrated can facilitate an easier blood draw.
By adequately preparing for your blood test, you increase the likelihood of receiving reliable results that accurately reflect your nutritional status.
How can you make sense of your blood test results concerning nutritional deficiencies?

Interpreting blood test results in the UK requires a thorough analysis of essential nutrient levels, such as iron and vitamin D. Unusual results may point to deficiencies that can lead to symptoms like chronic fatigue or weakened bone health. It is crucial to discuss any findings with your GP to fully understand their implications and determine the necessary actions to take.
Common indicators your GP will assess include:
- Low Iron Levels: This may suggest iron-deficiency anaemia, potentially requiring dietary changes or iron supplementation.
- Vitamin D Deficiency: Often linked with symptoms such as fatigue or bone pain, which may necessitate increased sun exposure or supplementation.
- Reduced Vitamin B12 or Folate Levels: Deficiencies in these nutrients can result in neurological symptoms and anaemia, requiring treatments such as injections or dietary modifications.
- High Levels of Certain Nutrients: Elevated nutrient levels may indicate toxicity or underlying health issues, necessitating further investigation and management.
Grasping these results is essential for creating effective corrective measures, which may include nutritional adjustments or supplementation tailored to individual requirements.
What are the most effective strategies for treating and preventing nutritional deficiencies?
In the UK, tackling nutritional deficiencies typically involves a combination of dietary modifications, vitamin supplementation, and professional medical guidance. For instance, increasing the intake of folate-rich foods, such as leafy greens and legumes, can significantly aid in rectifying deficiencies. Equally important are effective strategies for prevention.
These may include:
- Regular Check-ups: Scheduling blood tests according to your healthcare provider's recommendations can help identify deficiencies early on.
- Balanced Eating: Adhering to the NHS dietary guidelines ensures a varied intake of essential nutrients, contributing to overall health.
- Active Lifestyle: Participating in regular physical activity can enhance nutrient absorption and promote overall wellness.
- Educating Yourself: Acquiring knowledge about foods rich in essential nutrients fosters a proactive approach to maintaining optimal health.
By adopting a proactive mindset, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing deficiencies that could lead to long-term health complications.
How Does the Process of Blood Testing for Nutritional Deficiencies Work?
What is the step-by-step approach to blood testing?
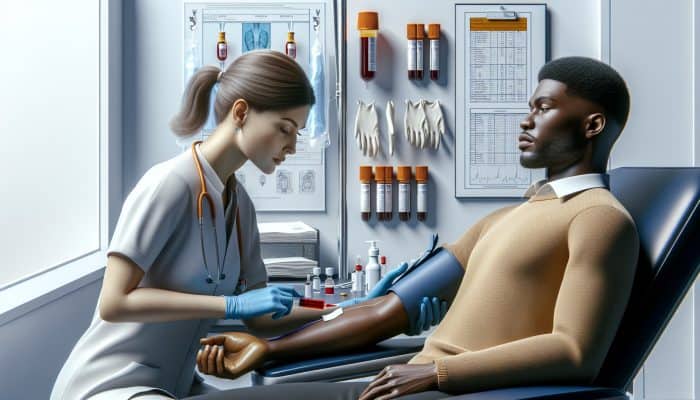
The process of blood testing to identify nutritional deficiencies is straightforward and typically encompasses several key steps to ensure accurate results. Initially, patients will schedule an appointment at a local clinic or hospital, often through the NHS or a private provider.
Upon arrival, healthcare professionals will conduct a brief interview to evaluate symptoms and gather medical history. Following this, a qualified phlebotomist will draw blood, typically from a vein in the arm, using a sterile needle and vial.
Once the sample is collected, it is labelled and dispatched to an accredited laboratory for analysis. The laboratory will measure specific nutrient levels, and results are generally available within a few days. Finally, patients will have a follow-up appointment to discuss their results and plan the subsequent steps in their healthcare journey.
What essential equipment and methods are utilised in blood testing?
Blood testing in the UK employs various equipment and methods to ensure accurate measurement of nutrient levels. The primary technique used is venipuncture, which involves inserting a needle into a vein to extract blood. This procedure requires skill and precision and is typically carried out by trained phlebotomists.
In laboratories, advanced equipment such as spectrophotometers and automated analysers are employed to quantify the concentrations of specific nutrients in the blood. These instruments yield rapid and precise results, which are critical for effectively diagnosing deficiencies.
Quality control plays a significant role in these processes. Accredited laboratories follow stringent protocols to ensure that each test remains reliable. This guarantees patients receive trustworthy information regarding their nutritional status, which is vital for facilitating effective treatment plans.
What results may suggest a problem with nutrient levels?
Blood test results can reveal potential nutritional deficiencies that may significantly impact a patient’s health. Low levels of essential nutrients often prompt further investigation and necessary interventions. For example, low iron levels, as indicated by serum ferritin tests, may suggest iron-deficiency anaemia, leading to symptoms such as fatigue and weakness.
Similarly, low vitamin D levels can result in complications related to bone health, while low vitamin B12 or folate levels may cause neurological symptoms. Recognising these deficiencies enables healthcare providers to develop targeted treatment strategies that effectively address them.
Patients should understand that abnormal results do not always indicate serious health issues. Regular monitoring and follow-up consultations can help individuals manage these deficiencies effectively, thereby improving overall health outcomes.
Expert Recommendations on Securing a Blood Test for Nutritional Deficiencies
What professional advice is available for selecting a testing provider?
Selecting a reputable provider for blood tests in the UK is essential for ensuring safety and accuracy. Experts suggest considering NHS services, which are generally free at the point of access, or accredited private clinics. When choosing a provider, look for those with positive reviews and regulatory recognition.
A practical starting point is to consult your GP, who can recommend trusted local services. When selecting a private clinic, verify its credentials and whether the laboratory is accredited by organisations such as UKAS (United Kingdom Accreditation Service).
Real-world examples include well-reviewed private clinics in major cities like London and Manchester that offer comprehensive testing services. These providers often feature transparent pricing and detailed explanations of their services, ensuring patients feel confident in their choice.
What common recommendations do experts provide for testing?
Experts in the UK frequently offer specific guidelines on when to order blood tests for nutritional deficiencies. For instance, it is advisable to get tested if individuals experience persistent symptoms such as fatigue, hair loss, or unusual bruising.
Moreover, those with dietary restrictions, such as vegans or vegetarians, may be at a higher risk for certain deficiencies and should contemplate regular testing. The NHS guidelines also recommend testing for individuals with chronic health conditions that may impact nutrient absorption, such as coeliac disease or Crohn’s disease.
Additionally, experts highlight the importance of routine testing as part of a proactive health strategy. Regular screening can identify deficiencies early, allowing for timely intervention and lifestyle adjustments that can significantly improve quality of life.
What advantages do professional guidelines emphasise regarding testing?
According to UK health authorities, the benefits of early detection through testing are considerable. Regular blood tests can uncover deficiencies before they escalate into serious health complications. This proactive approach allows for timely dietary changes or supplementation, promoting improved health outcomes.
Moreover, professional recommendations underscore the importance of consistent monitoring of nutrient levels for at-risk populations, including the elderly, pregnant women, and individuals with chronic illnesses. By adhering to these guidelines, individuals can minimise the risks of nutrient deficiencies, fostering a healthier life.
Experts assert that early intervention through testing not only enhances individual health but also alleviates the burden on healthcare systems by preventing chronic diseases linked to nutritional deficiencies.
What indications suggest the presence of nutritional deficiencies?
How can you identify early symptoms in your everyday life?
Recognising the early symptoms of nutritional deficiencies is vital for timely intervention. Common signs include chronic fatigue, muscle weakness, and frequent infections, which may indicate low levels of essential nutrients. Other symptoms, such as pale skin or hair loss, can also serve as significant warning signals.
Additional indicators to be mindful of include:
- Cracked lips or corners of the mouth: This may suggest deficiencies in vitamins, such as B vitamins, or in iron.
- Frequent muscle cramps: Often linked to magnesium deficiency.
- Slow-healing wounds: This may indicate a lack of vitamin C or zinc.
- Dry skin or brittle nails: These issues may suggest deficiencies in essential fatty acids or various vitamins.
By staying vigilant regarding these early signs, individuals can take proactive measures to seek testing and address any deficiencies before they evolve into more serious health concerns.
When should you seek medical advice regarding your symptoms?
If your symptoms persist or worsen, it is crucial to consult a GP in the UK to arrange for testing. Ongoing fatigue, unexplained weight loss, or changes in physical appearance may signify underlying deficiencies that necessitate professional evaluation.
Furthermore, individuals with a history of malabsorption disorders or those adhering to restrictive diets should not hesitate to seek medical advice. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can facilitate timely blood tests and help prevent long-term complications associated with nutritional deficiencies.
Ultimately, proactive engagement with healthcare is essential, especially for those experiencing symptoms that could suggest nutrient shortages.
How can you connect symptoms to specific nutrients?
In the UK, understanding how symptoms correlate with specific nutrient deficiencies can empower individuals to take appropriate action. For instance, signs such as pale skin are often associated with iron deficiency, prompting healthcare professionals to recommend targeted tests to support accurate diagnosis.
Other notable correlations include:
- Fatigue and Weakness: Commonly associated with deficiencies in iron, vitamin D, and vitamin B12.
- Hair Loss: May indicate deficiencies in essential fatty acids, proteins, or iron.
- Muscle Cramps: Often linked to magnesium or potassium deficiencies.
- Skin Issues: Dryness or rashes may indicate deficiencies in vitamins A, C, or E.
By recognising these connections, individuals can communicate more effectively with their healthcare providers, facilitating prompt testing and optimal treatment.
Evidence-Based Advantages of Blood Testing for Nutritional Deficiencies
What insights do recent studies provide?
Recent studies indicate that blood testing for nutritional deficiencies can significantly enhance health outcomes in the UK. Early detection allows for timely dietary interventions, thus improving energy levels and overall wellness. For example, individuals diagnosed with vitamin D deficiency frequently report improved mood and energy following the initiation of supplementation.
Research also suggests that identifying deficiencies can improve the management of chronic conditions. By addressing specific nutrient deficiencies, healthcare providers can assist patients in avoiding complications stemming from untreated deficiencies.
Real-world examples further underscore the importance of blood testing. Patients who underwent regular testing and subsequent treatment reported fewer health issues and significant improvements in quality of life, reinforcing the necessity for proactive health measures.
How does testing contribute to more favourable health outcomes?
Testing for nutritional deficiencies enables targeted interventions that enhance health and help prevent chronic conditions. Once diagnosed, healthcare providers can recommend dietary modifications or supplements tailored to individual needs. This personalised approach is vital for optimising health outcomes.
For instance, individuals with low folate levels may receive guidance on incorporating folate-rich foods, such as leafy greens and legumes, into their diets. Similarly, those with low vitamin B12 levels may be advised to increase their intake of animal products or consider supplementation.
Moreover, testing raises awareness of nutrition and personal health, empowering individuals to make informed choices about their diets and lifestyles.
What long-term benefits can arise from regular testing?
Engaging in regular blood testing for nutritional deficiencies can yield substantial long-term benefits. Establishing a testing routine allows for ongoing monitoring of nutrient levels, helping to prevent chronic health issues. For instance, regular checks can improve the management of conditions such as osteoporosis and anaemia by ensuring patients maintain adequate nutrient levels over time.
Research suggests that individuals who follow consistent testing schedules experience fewer health complications and improved overall well-being. This proactive health management approach can significantly enhance quality of life, reducing the risk of serious illnesses associated with nutrient deficiencies.
By prioritising regular blood tests, individuals can take control of their health, remain well-nourished, and minimise the risk of long-term health issues.
Why Is Prompt Detection Through Testing of Nutritional Deficiencies Crucial?
What are the potential consequences if deficiencies remain untreated?
Untreated nutritional deficiencies can result in severe health complications in the UK, including chronic fatigue, weakened immunity, and impaired cognitive function. For instance, untreated iron deficiency can progress to anaemia, resulting in debilitating fatigue and increased susceptibility to infections.
Additionally, long-term deficiencies can contribute to serious conditions such as osteoporosis, heart disease, and neurological disorders. By identifying and treating deficiencies early through blood testing, individuals can prevent these complications and maintain better health.
Ultimately, early detection is critical for minimising the risks of untreated deficiencies, facilitating timely interventions and necessary lifestyle modifications.
What significance does routine screening hold?
Routine screening is vital in identifying nutritional deficiencies before they escalate into more severe issues. For individuals in the UK, regular blood tests can detect nutrient deficiencies early, allowing for proactive management through dietary changes or supplements.
Healthcare providers recommend establishing routine screening schedules, particularly for high-risk populations such as the elderly, pregnant women, or those with chronic illnesses. By adhering to these schedules, individuals can maintain optimal health and prevent complications associated with nutrient deficiencies.
This proactive approach empowers individuals to take charge of their health, minimising risks and fostering long-term well-being.
How do testing options compare regarding effectiveness?
In the UK, comparing blood tests with alternative methods for detecting nutritional deficiencies reveals that blood tests are highly effective for both identification and management. Blood tests provide direct measurement of nutrient levels, facilitating precise diagnosis and personalised treatment plans.
In contrast, other methods, such as dietary assessments or symptom questionnaires, may not be as accurate. Blood testing is regarded as the gold standard for identifying deficiencies, enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions based on reliable data.
This effectiveness underscores the crucial role of blood testing in maintaining health and preventing chronic conditions associated with nutritional deficiencies.
How to Access Trustworthy Testing Services for Nutritional Deficiencies
What steps should you take to locate accredited labs in your vicinity?
When seeking reliable testing services, it is essential to find accredited laboratories in your area. In the UK, patients can access NHS-approved labs through their GP, ensuring that the testing process is secure and meets quality standards.
For those opting for private healthcare, researching local clinics accredited by organisations such as UKAS can provide further assurance regarding quality. Many reputable labs offer comprehensive information about their services online, enabling individuals to make informed decisions.
Additionally, local health directories often list accredited laboratories, making it easier to access services tailored to individual needs.
What are the costs and availability of testing through public services?
In the UK, public services such as the NHS provide affordable testing for nutritional deficiencies, making healthcare accessible to all. Many tests are available free at the point of access, although additional costs may apply for non-essential or private services.
Costs for private testing can vary significantly by provider and region. Comparing multiple options can assist individuals in finding services that fit their budget while ensuring accurate results.
Availability may differ by region, so it is crucial to consult local healthcare providers or online resources to understand the options available in your area.
What follow-up care is necessary after receiving results?
After blood testing, follow-up care is vital to ensure that individuals comprehend their results and take appropriate action. In the UK, patients typically schedule a follow-up appointment with their healthcare provider to discuss findings.
During this consultation, doctors will review the results, recommend treatment plans, and suggest dietary modifications as required. This appointment also serves as an excellent opportunity for patients to ask questions and address any health concerns.
Comprehensive follow-up care ensures that individuals remain informed and empowered to take control of their health, making necessary lifestyle and dietary adjustments based on their nutritional status.
What different types of testing services should you be aware of?
When seeking reliable testing services, it is essential to understand the various types available, including diagnostic, screening, and confirmatory tests. Diagnostic tests identify the underlying cause of specific symptoms, while screening tests help detect potential deficiencies in asymptomatic individuals.
Confirmatory tests validate prior results, ensuring accuracy before treatment begins. This knowledge helps you select the most suitable option for your specific needs, ensuring accurate results and appropriate follow-up care within the UK healthcare system.
Choosing the right testing service is essential for effective health management, empowering individuals to make informed decisions based on their unique nutritional needs.
How can you reach out to professional bodies for recommendations?
Professional organisations in the UK, such as the Royal College of Pathologists, can offer verified recommendations for trustworthy testing services. By reaching out, individuals gain access to accredited providers and valuable advice on selection, ensuring quality and safety in testing processes.
These organisations often publish lists of accredited laboratories and clinics, simplifying the search for dependable testing services. Accessing this information can enhance the safety and effectiveness of blood testing, ultimately benefiting overall health and well-being.
FAQs Regarding Nutritional Deficiencies and Blood Testing
What do nutritional deficiencies entail?
Nutritional deficiencies occur when the body lacks essential vitamins or minerals necessary for maintaining health, leading to various health complications.
Why is it essential to get tested for nutritional deficiencies?
Getting tested can identify deficiencies early, enabling timely dietary adjustments or supplements to enhance your overall health and well-being.
How is a blood test for nutritional deficiencies conducted?
A blood test typically involves drawing a sample from a vein in your arm, which is subsequently sent to a laboratory for analysis of nutrient levels.
Which nutrients are commonly tested for?
Commonly tested nutrients include iron, vitamin D, vitamin B12, folate, and calcium, among others, depending on your symptoms and risk factors.
How should I prepare for a blood test?
Preparation may include fasting, as instructed, and informing your healthcare provider of any medications or symptoms prior to the test.
What do low levels in a blood test signify?
Low levels can indicate nutritional deficiencies that may require dietary changes or supplements to address underlying health issues.
How frequently should I undergo testing?
It is advisable to be tested annually or more frequently if you have dietary restrictions or specific health concerns.
Can I access testing through the NHS?
Yes, the NHS provides blood testing services for nutritional deficiencies, often at no cost, through your local GP.
What treatment options are available for nutritional deficiencies?
Treatments may involve dietary adjustments, vitamin supplements, or lifestyle changes based on the specific deficiency identified.
What steps should I take if my test results indicate a deficiency?
Consult your healthcare provider to discuss the results and develop a treatment plan that may include dietary changes or supplements.
Join Us on Facebook!
This Article Was First Found On https://bloodtest.co.uk
The Article Blood Testing for Nutritional Deficiencies: A How-To Guide Was Found On https://limitsofstrategy.com
The Article Nutritional Deficiencies: Your Essential Blood Testing Guide found first on https://electroquench.com

